
IFMS AND GUJARAT: A CASE STUDY
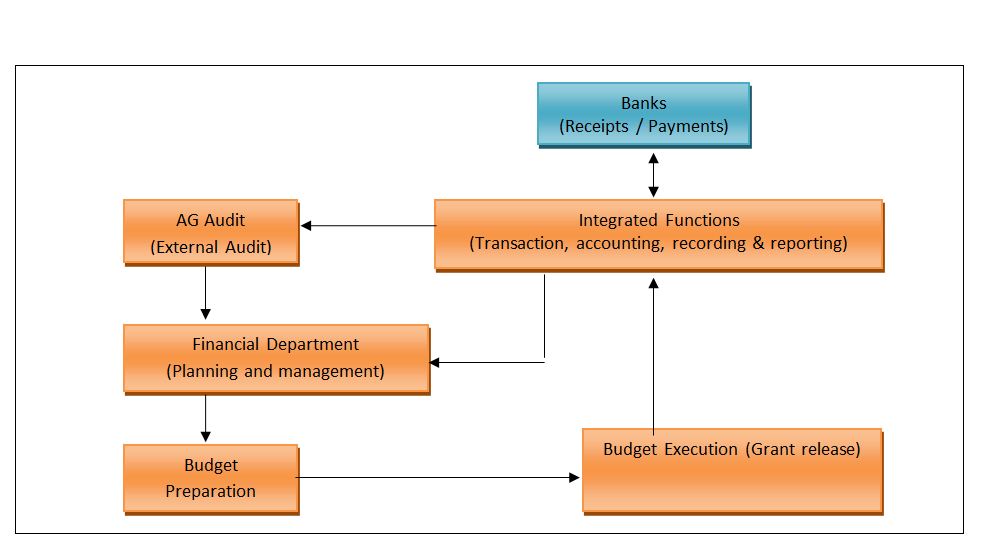
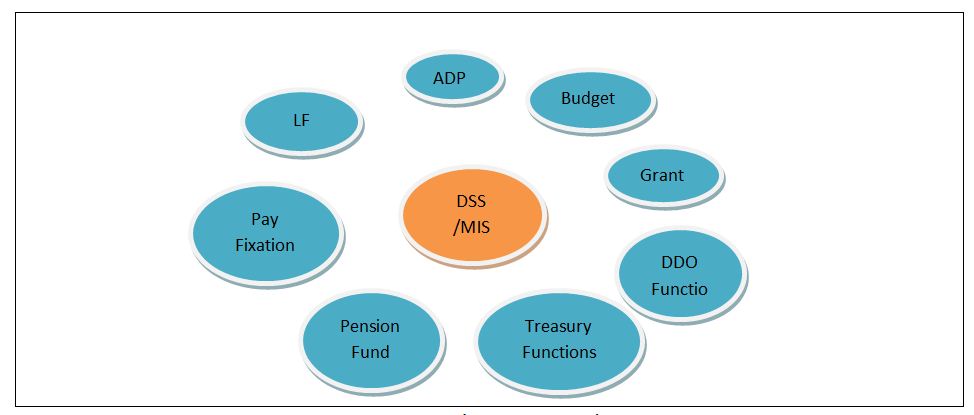
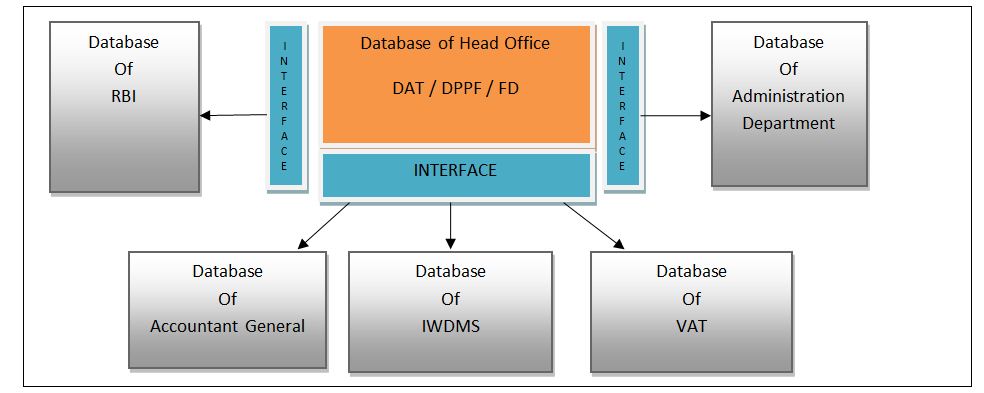
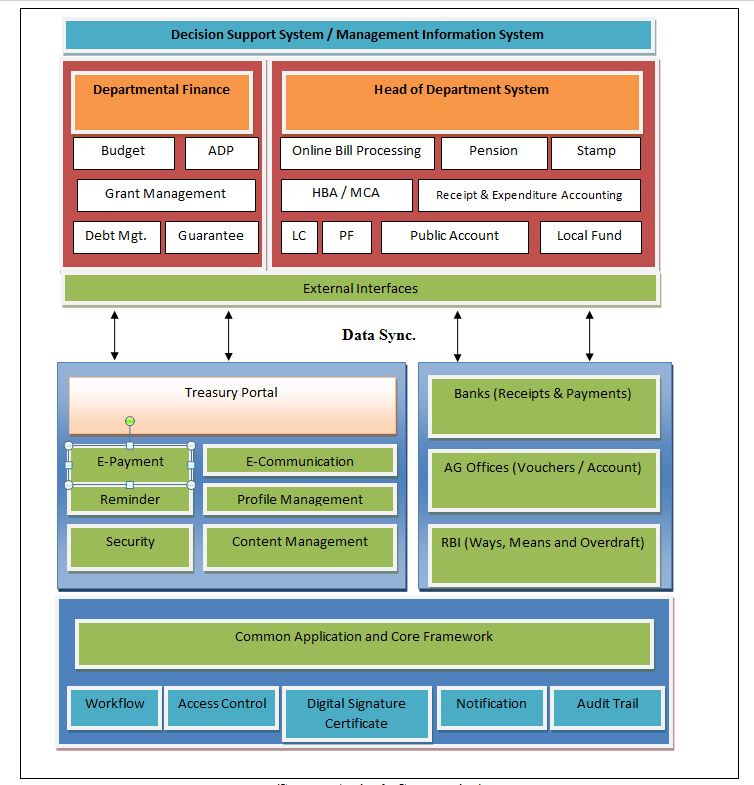
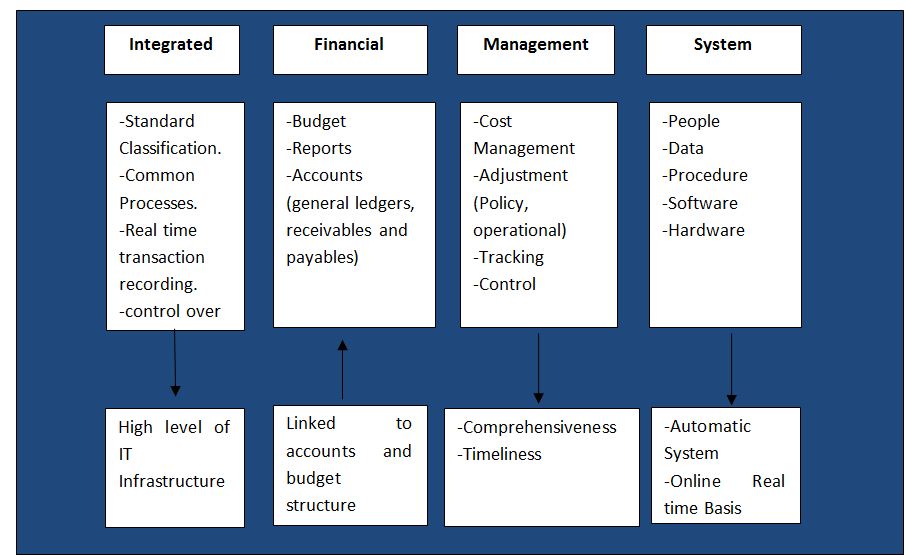
Abstract : Integrated Financial Management System (IFMS) is a platform for online computerized financial management that has adopted by Gujarat government recently, which has been proven important feature to this regional Finance Department of government. The IFMS came into existence due to the development of advanced information technology and the drawback of the existing manual system such as manual verification, time consuming process, lack of transparency, cumbersome paperwork and organization and storingof those documents etc. IFMS provides the information on a real time basis that is time saving and more efficient. IFMS serves as State's auditor by updating and managing receipt and expenditures on real time basis. Current IFMS application in Gujarat involves 8 modules (components) in its DSS and MIS; this application is fully automated and contains more than 200 reports and branch level registrations. The vision of the IFMS is to ensure careful and effective tracking and utilization of revenue, and disbursed grants. Online updating, fully automatic, fast, accurate, cross verification, e-payment, tracking of the particular transaction are some the plus points of this IFMS. Hence, The main benefit of this system is its transparency that can reduce the economic and social question of corruption. Currently, IFMS has been implemented and running successfully in several sectors of the Gujarat government. Although, the IFMS has a number of benefits yet its development is still in the infant stage and with many pitfalls in Gujarat. This article discusses the objectives, the level of implementation, pros and cons; and the possibilities of further development of IFMS in Gujarat. Key Words: Integrated Financial Management System, Gujarat, E-governance, Regional Financial System Developing regional E-governances are increasingly searching for the methods and the systems to improve and modernize its financial management system. There has been a prolusion of Integrated Financial Management System (IFMS) "a platform for online real time basis processing". IFMS aimed at accuracy, effectiveness, transparency, security of data and its scope and functionality varies across the country. In general terms IFMS refers to the automatic financial operations. IFMS can improve management of state by providing financial information to authority on real time basis and it will result into enhancement of decision-making capability. IFMS is a tool that provides integrated solution for consolidation and consistent information and data about the receipts and expenditures of the government. According to Dorotinsky (2003) and Rozner (2008), IFMS is an information system that tracks financial events and summarizes financial information also supports adequate management reporting, policy decisions, fiduciary responsibilities and the preparation of auditable financial statement. Rodin and Brown (2008) defined that IFMS is little more than an accounting system configured to operate according to the needs and specifications of the environment in which it is installed. It identifies the following features, which are the basic and necessary for integration. Lianzuala and Khawlhring (2008) in their research discussed that IFMS refers to the computerization of public financial processes from budget preparation and execution to accounting and reporting with the help of an integrated system for the purpose of financial management. IFMS of Gujarat government incorporates the major functions carried out by Finance Department, Directorate of Accounts and Treasury, Directorate of Pension and Provident Fund, Treasury and Sub treasury Offices, and Drawing and Disbursing Offices disseminated within the state. Even though IFMS is very useful and advantageous compare to the manual system, there are many obstacles and risk in its implementation. The success of IFMS in the various states depends on various factors of the regional economy. This article discusses the objectives, characteristics, components and the framework of IFMS in Gujarat including this; the article also focuses the status and the benefits of IFMS in the region, and the challenges in its implementation. The main vision of IFMS is to ensure scrupulous and effective recording and tracking of revenue, utilization of revenue and disbursed government grants to various department of Gujarat. And also to maintain effective control over the monitory position of the state, and it can be possible by effectively monitoring the revenues and expenditures of the Gujarat Government. Objectives The objectives for the implementation of IFMS by Gujarat government are as under. The Characteristics of IFMS To discover the characteristics of the efficient IFMS the research of Diamond and Khemani (2006, 99), and Chene (2009) found out that a well-designed IFMS contains the following characteristics. It is a management tool or system, providing the wide range of financial and non-financial information that indirectly hits the corruption. The main characteristics of IFMS found out by them are discussed here. 1. A Management Tool IFMS is a management tool because that helps the management to do control over the spending and its deficit, to achieve efficiency and fairness in allocation of resources. IFMS organizes the expenditure across policies, budgets, incentive programs and other projects so that the most important thing can be dealt the first. IFMS produces outcome at the lowest possible cost, also makes the better use of budgeted resources. And, by tracing the revenue, the utilization of revenue and disbursed grants through automated system, management is able to improve internal control, transparency, and accountability in the budget. 2. Provisions of Financial and Non Financial Information IFMS processes the data and generates variety of reports on budget, fund, treasury, cash flow, audit etc. IFMS provides not only financial but also the non-financial information. IFMS processes the various data and generates different kinds of accounts and financial statements. In these ways IFMS helps to build financial and not financial information for particular period and time. 3. A System and its Impact on Corruption The scope and functionality of IFMS have changed from the basic accounting application to a comprehensive system covering budgeting, collection of revenues, utilization of revenues, cash management, assets and liability, management etc. The IFMS played an important role to connect all the parties, to accumulate process and to provide information to all the parties, so it is also called mother system or central system. As discussed earlier the implementation of IFMS will result into accountability, transparency, and improved internal control. So the major benefit of IFMS is its impact on the corruption by increasing the risk of detection. By cross checking the transaction around the IFMS and by tracking the personal identification number detection of excessive payment, the theft and fraud can easily be detected. Chart 1.1 System of Financial Management (Source: Author's Construction) Chart 1.2 Components and framework of IFMS (Source: Author's Construction) The components shown in the chart are broadly discussed below. 1. ADP (Automatic Data Processing) As the name suggests ADP processes the data entered according to the nature of transaction and as per the trail of the system. All the necessary accounting and reporting functions of the entered data can be done with this ADP. 2. Budget The preparation of various type budgets, and revision of estimate can be possible by IFMS. It facilitates the effective and efficient utilization of funds of the state. Also this can be helpful for the comparison with the actual data. 3. Grants Various kinds of grants are given to control officers, departments and Drawing and Disbursing Officers etc. 4. DDO Functions (Drawing and Disbursing Officer Function) This component facilitated Submission of the online bills to treasury and tracking of the unutilized grants. 200+ reports and branch level registers can be maintained and generated. 5. Treasury Functions Treasury department performs the functions such as bill processing, stamp processing, pension payment processing, deposit in the beneficiary accounts and its accounting. 6. Pension Functions Directorate of Pension and Provident Fund Office performs functions related to pensions i.e. amount of pension, commutation, calculation of gratuity, PF account maintenance, preparation of new pension scheme etc. 7. Pay Fixation Pay fixation of employees as per designation, payment of salary, and verification of payment. 8. LF Audit (Local Fund Audit) Local Fund audit covers Pension processing of class IV and Panchayat employees, audit tracking of Panchayat. 9. DSS/MIS (Decision Support System/Management Information System) The reports can be generated for the state level, department level, scheme level, period wise and analytical based. External Interfaces Accountant General system, Banks, RBI, Citizen/Portals are the external interfaces which facilitates the receipts, payments, vouchers and Challans generation, financial and civil accounts preparation, revenue collection, payment details etc. Chart 1.3 IFMS Interfaces (Source: Author's Construction) Chart 1.4 The Structure of IFMS (Source: Author's Construction) Benefits of IFMS After studying the characteristics of the efficient IFMS, the article found out the advantages of IFMS from the literature review. Chart 1.5 Features of IFMS (Source: Author's Construction) The Challenges in the Implementation of IFMS Due to insufficient capacity the IFMS proved to be more complicated than what was originally envisaged. The Complex structure of IFMS requires more amounts of funds in development of system. The implementation of IFMS the needs change in management from the grass root level. Also the resistance to change is the general state of mind of people and convincing them to change the system is challenging task. The implementation of IFMS requires technical knowledge about the system and IT devices; government should expand funds for the training of IFMS to the employees working under IFMS. As IFMS is fully IT based system, the installation of various devices, networking and Internet around the connected departments requires huge amount of fund. Initially the procurement of funds and allocation of funds is the major challenge for this activity. The Status of IFMS in Gujarat Gujarat Government has implemented IFMS system in 26 District Treasury Offices, 2 Pay and Account Offices (Ahmedabad & Gandhinagar), 2 Pension Payment Offices (Ahmedabad and Gandhinagar), 145 Sub treasury Offices, Centralized Directorate of Pension and Provident Fund Office (DPPF), 25 Local Fund Offices, Centralized Pay Verification Unit (PVU). For this initiatives Gujarat government has received awards such as CSI, the Nihilent Awards of Excellence 2008-09 in the field of e-governance under department category by Computer Society of India and the EDGE Award 2010, by Information Week Edition Team, UBM Mumbai. Conclusion FMS is the tool, to provide the long-term solution for treasury and pension function, consolidation and consistent information about the revenues and expenditures of Gujarat Government, this system also helps in the tracking of the financial transactions and get us the various kinds of budgets, accounts and contains 200+ reports and branch level registers. The main benefits are accountability, transparency, and reduction in the level of corruption and fraud. But, the implementation of IFMS in Gujarat faces several kinds of obstacles such as lack of capacity, insufficient fund and other technical challenges for its success. Thus, the successful implementation of IFMS needs the capacity building program, availability of sufficient funds, strong human resource, project management, and efficient employees training program. Hence, if the Gujarat government can deals with these challenges the IFMS can be proved a vital tool for financial management reforms practices and further financial development of the region. REFERENCES :
***************************************************
Vanraj Aparnathi
Research Scholar,
S.D. School of Commerce,
Gujarat University.
Krishna Lala
Research Scholar,
Centre for Studies in Economics and Planning,
Central University of Gujarat,
Gujarat University.



Home | Archive | Advisory Committee | Contact us