
Need of Innovation in Marketing Stretegies as a Part of Economics Reforms
Introduction ::
A business unit does not have the objectives of earning profits only. Its objective is to earn profits by giving satisfaction to the customer. For this customers should be provide with right quality of product at the right time at right price and at right place. Now the sector of business s continuously changes out. Today the local market can be strive for global market because of acceptance of new reforms in industrial structure. The new economic reforms which lea to dynamic change in management structure is Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization. Because of this Marketing Management has been developed and it has got global acceptance.
For an organization to market a product effectively, they must first develop the product, and then apply the four key elements of the marketing mix to impact the development of the product and the marketing strategies. Understanding the how to develop a product is vital to any organizations marketing department. The marketing mix consists of product, place, price, and promotion. The 4 P’s of marketing essentially allow an organization to attract customers to the business.
Product :
The product is the service or good being offered to customers. Not only is the product or service going to attract the customer, but also what is offered along with the product. For example, when an organization new or old has developed a new product, the marketing department must think about the product packaging, features, options, services, warranties, and the product name.
Marketing Management :
Marketing Management is the analysis, planning implementation and control of programmers necessary to exchange the products and money with persons with their willingness.
According to WILLIAM STENTON, “Marketing Management includes all the activities connected with planning, pricing, promotion and distribution of products and services to satisfy current and prospective customers.
Marketing management is a programme for analyzing, planning, implementation and controlling mutually desired exchange between specific persons.
Marketing management is a socio-economic and managerial activity. Here there is a planned implementation of human relations and monetary exchange and other activities. The main purpose of exchange is to satisfy the need of both the parties. The need of the customer is to get a product while the main objective of the management is to make a long term profit through consumer’s satisfaction.
The present and future market in India is and would be a competitive market. With liberalization and globalization, competition is bound to increase. Larger quantity of goods at a lesser price and better quality will have to be provided for remaining in the market and for further development.
Elements of Marketing Mix :
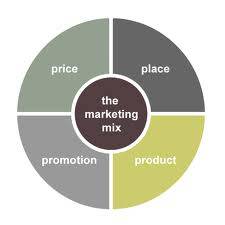
Product :
The term "product" refers to tangible, physical products as well as services. Here are some examples of the product decisions to be made:
Brand name
Functionality
Styling
Quality
Safety
Packaging
Repairs and Support
Warranty
Accessories and services
The product is the physical product or service offered to the consumer. In the case of physical products, it also refers to any services or conveniences that are part of the offering.
Product decisions include aspects such as function, appearance, packaging, service, warranty, etc.
Price :
Some examples of pricing decisions to be made include:
Pricing strategy (skim, penetration, etc.)
Suggested retail price
Volume discounts and wholesale pricing
Cash and early payment discounts
Seasonal pricing
Bundling
Price flexibility
Price discrimination
Pricing decisions should take into account profit margins and the probable pricing response of competitors. Pricing includes not only the list price, but also discounts, financing, and other options such as leasing.
Place of Distribution :
Distribution is about getting the products to the customer. Some examples of distribution decisions include:
Distribution channels :
Market coverage (inclusive, selective, or exclusive distribution)
Specific channel members
Inventory management
Warehousing
Distribution centers
Order processing
Transportation
Reverse logistics
Place (or placement) decisions are those associated with channels of distribution that serve as the means for getting the product to the target customers. The distribution system performs transactional, logistical, and facilitating functions.Distribution decisions include market coverage, channel member selection, logistics, and levels of service.
Promotion :
In the context of the marketing mix, promotion represents the various aspects of marketing communication, that is, the communication of information about the product with the goal of generating a positive customer response. Marketing communication decisions include:
Promotional strategy (push, pull, etc.)
Advertising
Personal selling & sales force
Sales promotions
Public relations & publicity
Marketing communications budget
Promotion decisions are those related to communicating and selling to potential consumers. Since these costs can be large in proportion to the product price, a break-even analysis should be performed when making promotion decisions. It is useful to know the value of a customer in order to determine whether additional customers are worth the cost of acquiring them.Promotion decisions involve advertising, public relations, media types, etc.
Different Approaches :
The 4 Ps is just one approach to the marketing mix. There are many other approaches.American author, Philip Kotler prefers the 4 Cs. He suggests that the 4 Ps are a seller's mix or sales orientated approach and it therefore should be replaced by the 4 Cs which are more customer orientated, or marketing orientated.
4 Cs stand for.......
Product = Customer Benefits
Price = Cost to Customer
Place = Convenience
Promotion = Communications
Going back to the 4 Ps, some feel this approach to the marketing mix misses the most important part of marketing; the centre of the marketing universe is omitted. The 5th P is the People: customers and employees. Customers are at the centre of the marketing universe.
Although the 4 Ps can be used for both products and services some feel that the 4 Ps works better for products than it does for services.
Four of the 7 Ps are the same. Product, Price, Place and Promotion
People, Process and Physical environment. Each of these Ps affects what the customer is offered. People are employees. Process means the production and delivery of the service. Physical Environment means the interior and exterior of the buildings.
In the recent times, 3 more P's have been included People or Personnel, Physical layout and Processes respectively.
The Marketing Mix :
Product :
The first P is Product. Product, in the most basic terms, could be defined as the unit that the business company wants to sell in the market. The business is equipped with marketing strategies to sell their products in the market. A notion developed in the earlier times that a good product will earn for itself does not hold good any longer. With a product boom in the market, it is evident that every product has a standard to maintain and it maintains it well, in order to survive in the market. Therefore, the layout of the product becomes very important. The product being offered to the customers should have its characteristics mentioned. This includes the direction of usage, date of manufacture and expiry, contents or ingredients, service, warranty. It should also include the distinguishing characteristics of the product. Every product should have a Unique selling proposition(USP). By this, we mean that the market is flooded with products of a kind, having different brand names attached. It is here that each product needs to be differentiated from the other. Thus, the concept of packaging and the phenomena of newness plays a vital role.At this stage, it is also important that we understand the dynamics and the nature of the product in question. Every product that the marketing strategist takes into consideration consists of realms or what we may refer to as 'levels' of a product. There are precisely three levels in a product. The core product, the actual product and the augmented product.
Core Product :
The core product is the inherent strata that makes possessing the product worthwhile. We are keen to possess a particular product because it boasts of benefits that are typical or novel to the product in question. The core level of the product is a component that you experience and may not be necessarily tangible. You buy a particular toothpaste due to its properties of fighting sensitivity in teeth. The benefit that you derive as a consumer is relief from the tooth ache and shock sensation when you eat something that either hot or cold. This benefit is exclusive to the product and may also be referred to as the USP or Unique Selling Proposition of the product.
Actual Product :
The actual level of the product is a tangible one, a component that you are aware of and are totally convinced by, due to its physical characteristics and overall appearance. The actual product may be referred to as a package that we are to carry along. It would be the toothpaste that you would buy, use and derive the benefits from.
Augmented Product :
The augmented level of the product is the upper crust of the product. This feature involves the coverage that you receive along with the product. Guarantee and warranty period, the after sales services, product feedback cells, the process of installation or the direction of use are characteristics that may be found in the realm of the augmented product.
Tools for Evaluating a Product :
Product Life Cycle (PLC):
Another marketing tool for evaluating a product in question is termed as Product Life Cycle or PLC. It is called so because it has a process that is staunchly followed by a product. There is indeed no paradigm shift that the product incurs. One may draw parallels between the human and product life cycle. The basic similarities that we notice are the stages of development; just as human beings have stages of being a neonate, developing into an adolescent, followed by youth, adulthood, middle age and old age; according to the PLC theory products have a cycle where they are launched into the market zone, are given the time and promotion for growth, experiencing a peak in their market status followed by the maintenance period, consequently diving into the declining sector also leading to backing out on the product. However, let's make it very clear, that all products do not follow the same routine of maturity and fall in the market arena. It may be very likely that the product may skip the betwixt stages altogether and hop from its launch and dive straight into a decline and finally withdrawal stage. Thus, it would be practically defective an inference to put forth that all products carry with them a fixed-cum-mandatory life cycle to adhere to.
Customer Life Cycle (CLC):
The next marketing tool to be discussed in connection to product is termed as Customer Life Cycle, abbreviated as CLC. In theory, the concept runs in conjunction to that of PLC. The customer life cycle looks at the services and products that it can offer the customer and thereby fulfill their needs, preferably for a lifetime. The basic similarity between PLC and CLC is that of the array of growth however with differential variables being involved. Where PLC concentrates on tracking the velocity of growth leading to maturity of the product in the market; CLC is developing and maintaining the relationship between the customer and the organization. It is important to spell out that the customer life cycle may not remain common for all products and services, as each company is catering to different set of needs of the customers. Thus, in such a case, it is virtually unrealistic to compartmentalize the guidelines that are followed by all products.
Price:
The second component is Price. Price is the amount the company will charge for offering the product to the customer. Pricing is considered to be an important step of marketing mix. The pricing should be according to what the product has to offer. If the pricing of a particular product is too low, the general tendency of the customers that the product is of sub-standard quality, reflects in the sale. On the other hand, if the pricing is too high, not many people would be interested in buying the product. The price tag scares them off. A flip side to this is the consumer behavior.
Place:
The place factor too contributes to the marketing mix. The availability of the product at the desired time and the desired place is what the marketing strategy focuses on. Placement strategy becomes mandatory as the products need to be available to the customers when they want them. A part of the placement strategy is to get the shopkeeper or retailer to notice your product and provide it with a prominent space or shelf . This increases the probability of the product getting sold. This encourages the customer to pay heed to the product. The visibility of the product becomes a point where sale could take place.
Promotion:
The fifth component that answers 'what is marketing mix' and a stage where the product finally goes on the floor is Promotion. The act of promotion involves publicizing the product. Masses come to know about the product's existence through promotion. Magazines, newspapers, television are the popular modes of conducting promotion. Another mode that has joined this popular bandwagon is on-line marketing services. The Internet is cheap and highly effective. The promotion activity is now a full-fledged gimmick that elevates the interest of the consumer by devising certain clues and hints that characterize the product. This is done before the product is physically launched in the market. This tactic increases the curiosity of the consumer and gets him excited to discover what the product has to offer.
People or Personnel:
To include people as the component of a marketing mix becomes very essential. It is the people who make services and products a success and they are the ones who have the power to tarnish the image of the product. People like to communicate or interact with people who are courteous in nature. The attitude and the behavior of the employees makes a lot of difference.
Physical Layout:
There were times when customers and clients did not come in direct contact with the retailers, but now times have changed. Customers do come in contact with the retailers and pay attention to the physical qualities of the shop. The appearance of the outlet, style of presentation and the easy accessibility of products are prerequisites to crown the shop with the tag of having an attractive and appealing physical outlook. In terms of services, customers do require a standard to be maintained. For instance, students who procure admission in a reputed college, have high expectations in terms of the quality of education, faculty and the facilities, amenities and opportunities provided by the institution for an all round development.
Process:
Processes are an important element of the marketing mix. It is a component that makes marketing work effectively and proficiently in an organization. Processes, to explicate a few, include, dealing with customer complaints, interacting with customers and understanding their focal requirements and demands and handling orders received by customers.
Limitations of the Marketing Mix Framework
The marketing mix framework was particularly useful in the early days of the marketing concept when physical products represented a larger portion of the economy. Today, with marketing more integrated into organizations and with a wider variety of products and markets, some authors have attempted to extend its usefulness by proposing a fifth P, such as packaging, people, process, etc. Today however, the marketing mix most commonly remains based on the 4 P's. Despite its limitations and perhaps because of its simplicity, the use of this framework remains strong and many marketing textbooks have been organized around it.
***************************************************
Prabhu Karan J
PhD. Research scholars J.J.T University Rajasthan
E-mail: karan_prabhu2005@yahoo.com
Mob. 9898173630
&
Bhadauria Manish K.
PhD. Research scholars J.J.T University Rajasthan
E-mail: mannthakur03@yahoo.co.in
Mob. 9016265376



Home | Archive | Advisory Committee | Contact us