Cloud Computing in Libraries
Abstract ::
Cloud computing is a new technology model for IT services. This technology is mainly used by many businesses and organizations. It facilitates its users to avoid locally hosting multiple servers, devices, equipments and constantly dealing with hardware failure, software installs, upgrades and compatibility issues. For many organizations, cloud computing can simplify processes and save time and costs and workflows they have. This article defines Cloud computing, its characteristics, service models and deployment of cloud services, its advantages in libraries and the potential areas mainly technology, data and community for improvement.
INTRODUCTION ::
Pertaining to the 5th law of library science, library is a growing organism. Today we are living in the age of information and with modern technology. A well equipped library is the heart of any higher education and also helpful for the growth of national economy by providing information on time. Internet is one of the greatest technologies of this millennium; it revolves around advancements in ICT applications in all the area of our routine work. Library is place where information is gathered, stored and retrieved by the patrons. Now-a-days information is available only on online and in digital format and the need of information is high. So the librarian should use the modern technology to store the digital information in a wide number which can be retrieving by various users. Such technologies are Web 2.0, server virtualization, cloud computing etc… And this technology can be used to store more information at libraries as content creation, storage, e-learning, archives etc… Data storage is the basic task of any library; hence this paper gives the clear picture of impact of cloud computing at libraries.
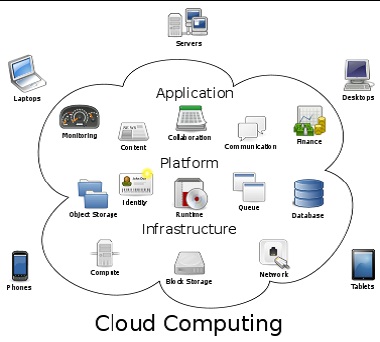
What is Cloud Computing ?
Cloud computing can be understood as a way to use off-site computer processing power to replace content creation and servers that were traditionally hosted onsite. In layman’s terms this means “using Web services for our computing needs”. Cloud computer allows content creation to be made “when data and software applications reside on and are drawn from the network rather than locally on any one workstation”. By utilizing online applications, users can create and save their files online, share content (often for free!), work collaboratively with others or create entire services that can all be accessed online without need of having the programs on their own computer. These online services can reduce the need for expensive software, hardware, and even advanced technical knowledge from library staff since cloud computing services are often streamlined to be very user-friendly. As well, “the focus shifts away from which devices effectively store data and able to run applications to which devices can provide the easiest access to data and applications – which are stored at various places on the Internet”.